

Embryology from internal urethral meatus to sinus pocularies (uterus masculinus) the urethra is developed from urogenital diaphgram sinus portion of male urethra correspond to the entire female urethra from sinus pocularies to fossa navicularies the male urethra is formed by the fusion of the edges of medial labial fold which also form carpous spongiosum the urethra transversing the glans is the last to be developed is formed by the down growth of a solid pencil of ectoderm, which become canalised shortly before birth.
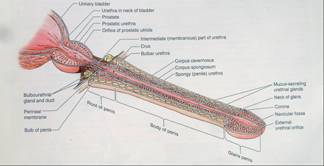
Male urethra is 18 to 20 cm long extended from an internal orifice in the urinary bladder to ext opening or meatus at the tip of penis.
It may be considered into three regional parts -
And present a double curve in the ordinary flaccid state of penis.
It is widest and most dilatable part of urethra and about 3 cm long. It runs almost vertically through prostate. It is wide in middle and narrow below. On section it is cresentric, convex vertically due to presence of posterior wall of narrow median longitudinal ridge form by elevation of the mucus membrane and its adjacent turn, termed as urethral crest. On each side of crest there is shallow depression, prostatic sinus the floor which is perforated by orifice of prostatic duct about middle elevation on which the slit like orifice of prostatic utricle is situated. On each side of this orifice or just with in this orifice there is small opening of ejaculatory duct.
The prostatic utricle is a 6 mm long sac situated upward and backward into prostatic substances and behind the median lobe.
Shortest, least dilatable and narrowest portion of urethra (except the external orifice) it descends with slight ventral concavity from prostatic to bulb of penis, passing through perineal membrane about 2.5 cms posterioinferior to Pubic symphysis. It is 1.25 cm to 2 cm in length. The membranous urethra is surrounded by fibres of urethral sphincter on bulbo urethral gland is sited on each side of this part of urethra.
It is continued in carpous spongiosum of penis. It is about 15 cm long and extends from the end of membranous urethra to external urethral orifice i.e. on glans penis it continues vertically concave curve of membranous urethra to a point anterior to lowest level of symphysis pubis. From here when the penis is flaccid it curve downward in the free part of penis. It is narrow with a uniform diameter of about 6 mm in penis. It is dilated at its commencement as interbulbar fossa. The bulbo urethral glands open into the spongiose of urethra about 2.5 cm below the perineal membrane.
External urethral orifice except in its most anterior part, presents the orifice of numerous small mucous glands and follicles situated into the submucous tissues and named urethral glands. Besides these there are a number of small pit like recesses or lacunae of varying sizes the opening of which directed anteriorly.
On larger lacuna, the lacuna magna is situated on the roof of the navicular fossa.
Two sphincters surround the urethra. The internal vesical sphincter controls the neck of the bladder and prostatic urethra above the opening of the ejaculatory ducts. It is composed of non-striated muscle is not under the voluntary control and is supplied by sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres derived from vesical plexus.
The external urethral sphincter surrounds the membranous urethra and consists of striated muscle it is supplied by perineal branch of pudendal nerve (S 2, 3, 4,) and under voluntary control.
Male Urethral Structure:
The urethra is composed of mucus membrane supported by submucous coat (tissue) which connects it with various structures through which it passage.
The mucus membrane of the urethra is continues internally with that of bladder and externally with skin covering glans penis. It is prolonged into the duct of urethral, bulbourethral, prostatic gland and into the different ducts and seminal vesicles through the ejaculatory duct. In membranous and spingiose urethral region it is arranged into longitudinal folds when urethra is empty.
The urethral epithelial lining is transitional variety as far as ejaculatory duct there after it is composed of patches of pseudostratified columnar and stratified epithelium amongst which are situated diverticula of various sizes, some extending into the lamina propria as mucous glands, near the external urethral orifice the epithelium is stratified squamous in type.
The submucous tissue consist of a vascular erectile layer outside this there is a layer of non striated muscular fibres, arranged into an inner longitudinal and outer circular layer and best marked in the prostatic and membranous urethra.